-40%
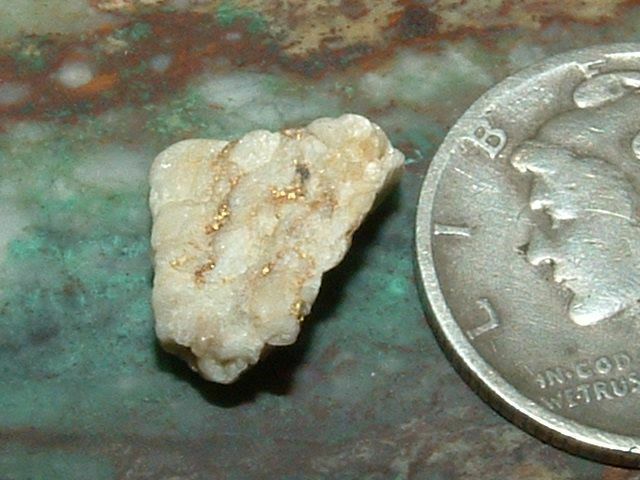
Rhenium 99.95% Pure Rare Genuine
$ 184.8
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Arguably the most authoritiative source of geological information, the Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, lists rhenium as the rarest of the stable elements in the Earth’s crust at just 700 parts pertrillion
. While this stat is contested (other sources point to osmium or iridium) the fact is that this metal is in exceptionally short supply. And though it’s far, far rarer than gold it’s also just a fraction of its price.
This lopsided relationship may not last for much longer. With an estimated annual production of fewer than 50 tons there is precious little wiggle room on the supply side. Yet, attention to its potential has been called by major media outlets like Reuters, Bloomberg and even a spotlight in a BBC documentary titled “Secrets of the Super Metals” there is a near-certainty that in the years to come more buyers will want to take a ride on the rhenium bus.
Rhenium
is a
chemical element
with the
symbol
Re
and
atomic number
75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row
transition metal
in
group 7
of the
periodic table
. With an estimated average concentration of 1
part per billion
(ppb), rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the
Earth's crust
. Rhenium has the
third-highest
melting point
and highest boiling point of any stable element at 5869 K.
[4]
Rhenium resembles
manganese
and
technetium
chemically and is mainly obtained as a
by-product
of the extraction and refinement of
molybdenum
and
copper
ores. Rhenium shows in its compounds a wide variety of
oxidation states
ranging from −1 to +7.
Nickel
-based
superalloys
of rhenium are used in combustion chambers, turbine blades, and exhaust nozzles of
jet engines
. These alloys contain up to 6% rhenium, making jet engine construction the largest single use for the element. The second-most important use is as a
catalyst
: rhenium is an excellent catalyst for
hydrogenation
and isomerization, and is used for example in
catalytic reforming
of naphtha for use in gasoline (rheniforming process). Because of the low availability relative to demand, rhenium is expensive, with price reaching an all-time high in 2008/2009 of US,600 per
kilogram
(US,800 per pound). Due to increases in rhenium recycling and a drop in demand for rhenium in catalysts, the price of rhenium has dropped to US,844 per
kilogram
(US,290 per pound) as of July 2018